Workflow Automation
Workflow Editor
The Workflow Editor is the central environment for creating, managing, testing, and executing workflows. Within the Workflow Editor app, you can design and refine workflows, then export them as JSON files for use with the Workflow Runner.

Figure: In Workflow Editor app, you can create/refine/export/import a workflow.
Workflows
A workflow is a structured sequence of actions or tasks that are executed step by step to achieve a specific outcome. In automation systems, a workflow typically consists of a list of predefined activities—such as reading data, clicking buttons, entering text, or processing information—that are carried out in order, one after another. Each action depends on the completion of the previous step, creating a logical flow from start to finish.
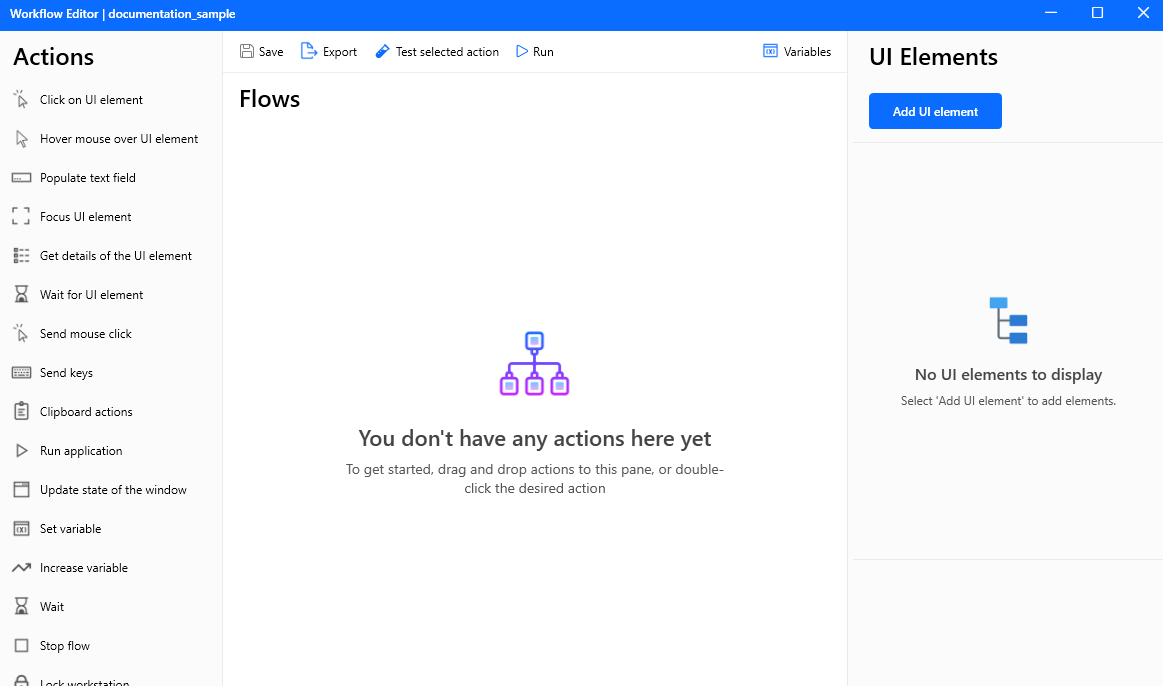
Figure: Workflow environment including various actions.
Export a Workflow
To export a workflow in the Workflow Editor app, select it from the list and click the Export button on the right side. The workflow can be exported and stored on your PC or other systems in two formats. Use .json to run it via Accesskey scripts, or use .idwf to be able to import it later into Workflow Editor.
Import a Workflow
To import a previously saved workflow, click the Import workflow button and select an .idwf file. The imported workflow opens in Workflow Editor, where you can review, edit, test, and export it again.
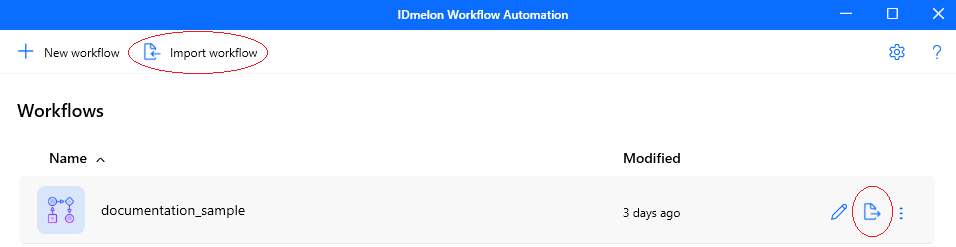
Figure: The specified buttons can be used to export/import a workflow.
Startup behavior for Workflow Runner
In Settings (at the top right corner of the workflow editor), Workflow Runner startup behavior can be configured using one of these options:
- Do not run at startup
- Run at startup
- Run at startup as administrator
To enable Run at startup as administrator, follow these steps:
- Close Workflow Editor (if it is running).
- Right-click Workflow Editor and select Run as administrator.
- Open Settings and select Run at startup as administrator.
Note: Administrator permissions are required to apply this option. If Workflow Editor is not started as administrator, the setting may not be applied.
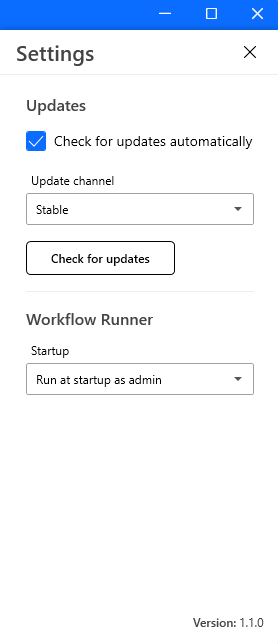
Figure: The expanded view of the settings menu.
Actions
There are two types of actions:
- Element-based actions: These actions depend on UI elements and operate on a specific element (e.g., clicking a UI element).
- Non-element-based actions: These actions are not tied to UI elements and perform operations directly on the system (e.g., running an application).
Available actions are listed below.
Click on UI element
Simulates a mouse click on a specified UI element, allowing the automation process to interact with buttons, links, checkboxes, or other clickable components within the application interface.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to click. |
| Click type | Enum | Yes | Left click | Allowed: Left click, Double click, Right click |
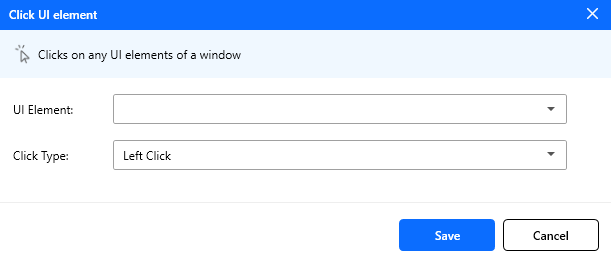
Figure: Click on UI element action configuration.
Hover mouse over UI element
Moves the cursor over a UI element.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to hover over |
Populate text field
Fills a text field with the entered text.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target text field to populate |
| Text to fill-in | String | Yes | Empty | The text to enter in the text field |
Note: This action can be applied only to Inputs.
Note: You can use variables instead of static strings. For more details, see variables.
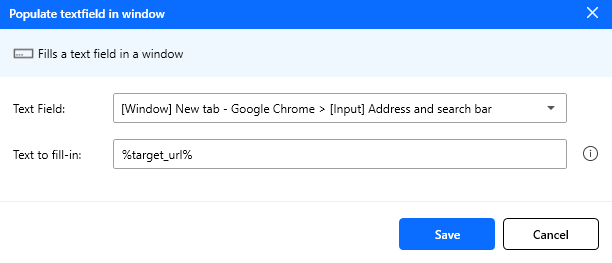
Figure: Populate text field action configuration.
Focus UI element
Sets the focus on a UI element.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to set focus on |
Get details of the UI element
Gets the value of a UI element’s attribute.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to read details from |
| Attribute name | Enum | Yes | Id | Allowed: Id, Name, Class, Enabled, … |
| Bind to variable | String | Yes | Empty | The variable name where the attribute value is stored |
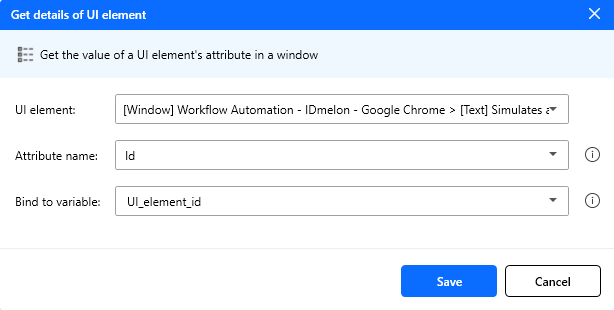
Figure: Get details of the UI element action configuration.
Wait for UI element
Waits until a UI element appears on screen.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to wait for |
| Timeout | Number (Double) | Yes | 10 | Maximum wait time (in seconds) for the element |
Send mouse click
Sends a mouse click event.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse event | Enum | Yes | Left click | Allowed: Left click, Double click, Right click |
| Delay | Number (Int) | Yes | 0 | Delay before sending the mouse event (milliseconds) |
Send keys
Sends keys to the UI element that is currently focused.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text to send | String | Yes | Empty | The text to send to the focused element/window |
| Delay | Number (Int) | Yes | 10 | Delay between keystrokes (milliseconds) |
To simulate a key press, use curly brackets {} (e.g., {enter}). For key combinations, wrap both keys in {} (e.g., {leftctrl}({A})).
Note: You can insert modifiers or special keys using two combo boxes at the bottom of the text field.
Note: For the modifiers, the second key must be added inside a ({}) (e.g., {leftctrl}({A}) for the select all shortcut).
Note: You can also use variables as a part of the text (See Variables).
Some common shortcuts:
- Select all: {leftctrl}({A})
- Copy: {leftctrl}({C})
- Paste: {leftctrl}({V})
- Shift Delete: {rightshift}({delete})
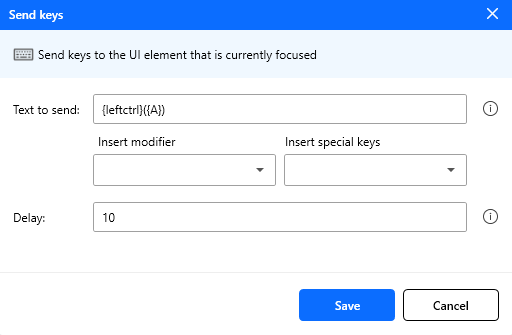
Figure: Send keys action configuration.
Run application
Executes an application.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application path | String | Yes | Empty | The executable file path |
| Command line arguments | String | No | Empty | Additional arguments passed after the executable name |
| Working folder | String | No | Empty | The working directory path for the application |
| Window style | Enum | Yes | Normal | Allowed: Normal, Hidden, Minimized, Maximized |
| After application launch | Enum | Yes | Continue immediately | Continue immediately, Wait for application to load, Wait for application to close |
If you want to use the ExitCode variable for next actions, set the After application launch option to Wait for application to load.
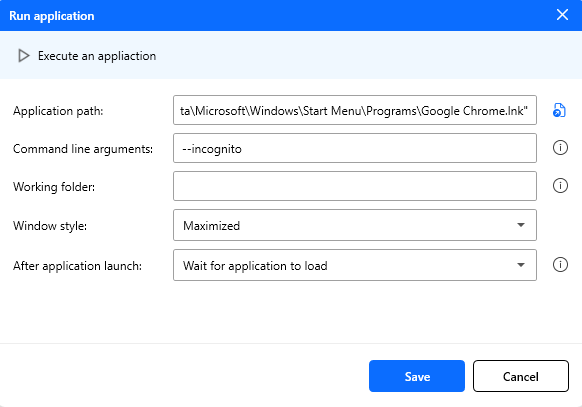
Figure: Run application action configuration.
Update state of the window
Updates the state of one or more windows that match the specified search criteria.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Find window mode | Enum | Yes | By window UI element | Allowed: By window UI element, By title or class |
| Window | UI element | No | Empty | Target window UI element (used when mode is By window UI element) |
| Window title | String | No | Empty | Window title (used when mode is By title or class), supports ? and * |
| Window class | String | No | Empty | Window class (used when mode is By title or class) |
| Window action | Enum | Yes | Focus on window | Allowed: Focus on window, Move to background, Maximize window, Minimize window, Close window |
Note: If multiple windows match the criteria, use When multiple match to control whether the action is applied to the first match only or to all matches.
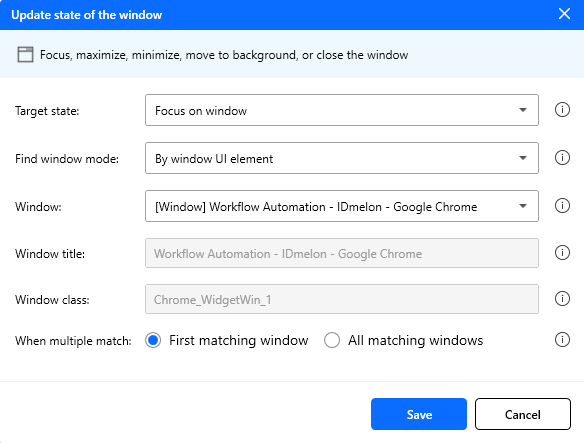
Figure: Update state of the window action configuration.
Set variable
Set the value of a new or existing variable, create a new variable or overwrite a previously created variable.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | String | Yes | Empty | A variable name (existing or new) |
| Value | String/Int/Double | Yes | Empty | The value assigned to the variable |
Note: You can use variables in the form of %variable_name% for assigning values. For more details, see variables.
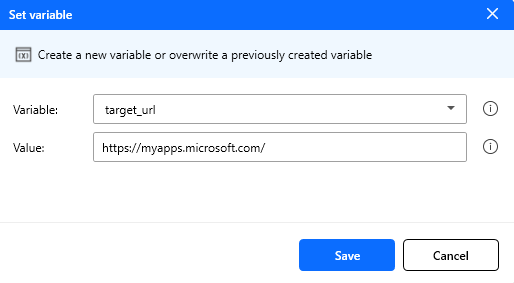
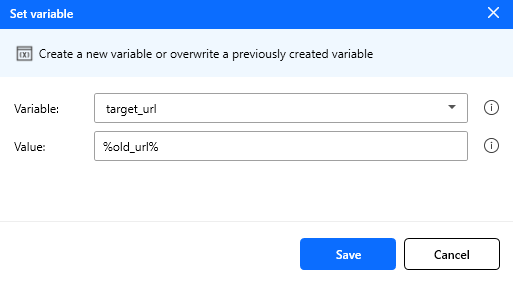
Figure: Set variable action configuration.
Increase variable
Increases the value of a variable by a specific amount.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable name | String | Yes | Empty | The numeric variable to increase |
| Increase by | Number (Int/Double) | Yes | Empty | A numeric value or a variable containing a numeric value |
Note: Negative numbers can also be used to decrease the value of a variable.
Wait
Suspends the execution of the flow for a specific amount of seconds.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | Number (Double) | Yes | Empty | The duration in seconds |
In addition to numbers, you can also make use of variables (See Variables).
Stop flow
Terminates the flow.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With status | Enum | Yes | Success | Allowed: Success, Failure |
Lock workstation
Locks the workstation’s display.
Input Parameters:
No inputs needed.
Call Accesskey function
Calls an Accesskey function and retrieves its result.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function name | String | Yes | Empty | The Accesskey function name to call |
Note: To test the function and see the result, after selecting the function and filling the required inputs, click on the Test button next to the function’s drop-down.
Note: A badge (or a card) must be cached during execution. So you need to tap your badge on the reader before testing this action.
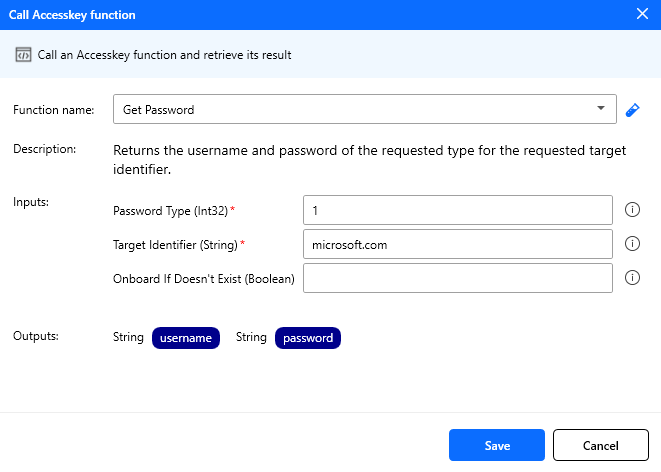
Figure: Call accesskey function action configuration.
Run PowerShell script
Executes some custom PowerShell script and retrieves its output into a variable.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Script | String | Yes | Empty | The PowerShell code to execute (variables are resolved beforehand) |
| Timeout | Number (Double) | Yes | 0 | Maximum wait time in seconds (0 means no timeout) |
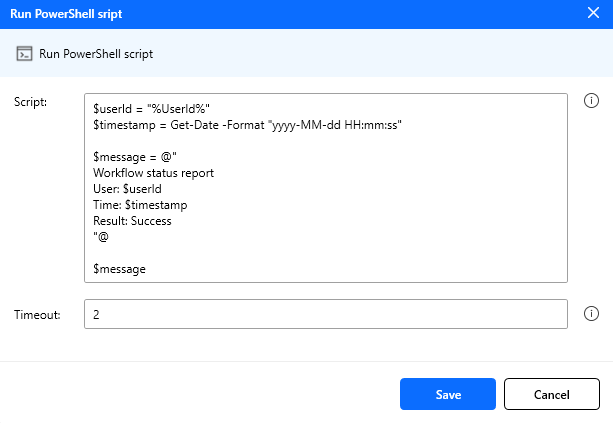
Figure: Run powershell script action configuration.
Conditional Actions
Conditional actions are workflow steps that execute only when specific conditions are met. They are useful for tasks like checking the value of a variable, verifying whether an element exists on screen, or controlling the flow of automation based on dynamic criteria.
If
Checks if two values match.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The first value, variable, or expression to compare |
| Operator | Enum | Yes | Equal to (=) | Comparison rule between first and second operands |
| Second operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The second value, variable, or expression to compare |
Allowed operators: Equal to (=), Not equal to (!=), Greater than (>), Greater than or equal to (>=), Less than (<), Less than or equal to (<=), Contains, Does not contain, Starts with, Ends with, Is empty, Is not empty.
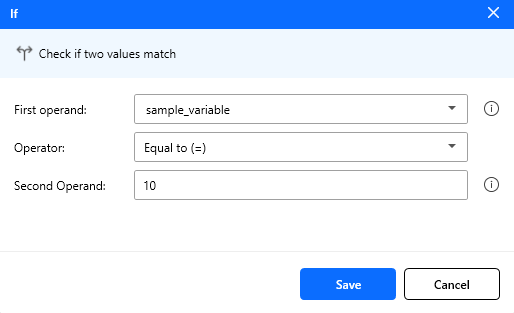
Figure: If conditional action configuration.
Else if
Starts a block of actions that run only if earlier If or else if checks fail, and this condition is true.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The first value, variable, or expression to compare |
| Operator | Enum | Yes | Equal to (=) | Comparison rule between first and second operands |
| Second operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The second value, variable, or expression to compare |
Allowed operators: Equal to (=), Not equal to (!=), Greater than (>), Greater than or equal to (>=), Less than (<), Less than or equal to (<=), Contains, Does not contain, Starts with, Ends with, Is empty, Is not empty.
Else
Starts a block of actions when none of the preceding if or else if conditions are met.
Input Parameters:
No inputs needed.
If UI element exists
Checks whether a UI element exists on the screen.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI element | UI element | Yes | - | The target element to check |
| If UI element | Enum | Yes | Exist | Allowed: Exist, Doesn’t exist |
| Timeout | Number (Double) | Yes | 2 | Search timeout in seconds |
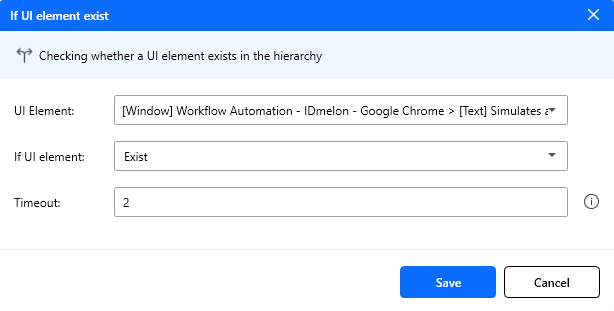
Figure: If UI element exists action configuration.
Loops
Loops are workflow actions that repeat a set of steps until a specified condition is met. They are useful for iterating over collections or repeatedly checking values.
For loop
Iterates a block of actions for a specific number of times.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start from | Number (Int) | Yes | Empty | The starting value of the loop counter (variables allowed) |
| End to | Number (Int) | Yes | Empty | The ending value of the loop counter (variables allowed) |
| Increment by | Number (Int) | Yes | Empty | The increment step for the loop counter (variables allowed) |
Note: You can use variables instead of static numbers. For more details, see Variables.
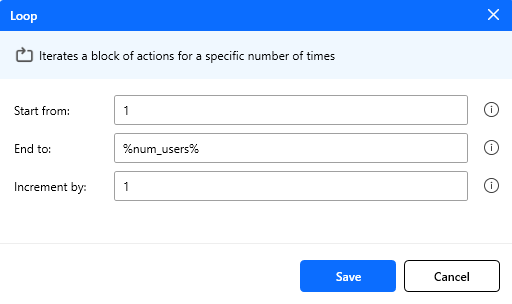
Figure: For loop action configuration.
Loop condition
Iterates a block of actions as long as a specific condition proves to be true.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The first value, variable, or expression to compare |
| Operator | Enum | Yes | Equal to (=) | Comparison rule between first and second operands |
| Second operand | String/Number | Yes | Empty | The second value, variable, or expression to compare |
Allowed operators: Equal to (=), Not equal to (!=), Greater than (>), Greater than or equal to (>=), Less than (<), Less than or equal to (<=), Contains, Does not contain, Starts with, Ends with, Is empty, Is not empty.
Next loop
Used inside a loop to skip the current iteration and jump directly to the next one when certain conditions are met.
Exit loop
Immediately terminates a loop when a specific condition is met, stopping any further iterations.
Read CSV from file
Reads a CSV file from your PC or system and loads it into a data table variable.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSV file path | String | Yes | Empty | Full path to the .csv file to read (you can also use the select file button on the right side for convenience) |
| First line is header | Boolean | No | false | If enabled, the first row is treated as column names; otherwise, columns are auto-named (Col 1, Col 2, …) |
| Trim fields | Boolean | No | false | If enabled, trims leading/trailing spaces for each field value |
| Store result in | Variable | Yes | Empty | Name of the variable that receives the output DataTable |
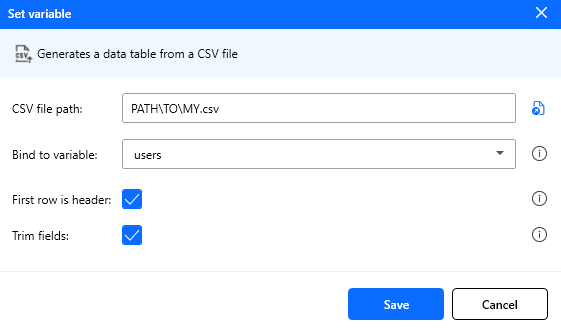
Figure: Read CSV from file action configuration.
Find in data table
Searches a column in a source data table and stores matching rows in a new data table variable.
Input Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data table | Variable | Yes | Empty | Source variable containing the input DataTable |
| Text to find | String | Yes | Empty | Text to search for in the selected column. Supports variable placeholders |
| Column name or index | String | Yes | Empty | Target column by exact name or zero-based index (0, 1, …) |
| All matches | Boolean | No | false | If enabled, returns all matching rows; otherwise, returns only the first matching row |
| Match case | Boolean | No | false | If enabled, text comparison is case-sensitive |
| Match entire cell | Boolean | No | false | If enabled, value must match the full cell text; otherwise, substring matching is used |
| Store result in | Variable | Yes | Empty | Variable name that receives the output DataTable with matched rows |
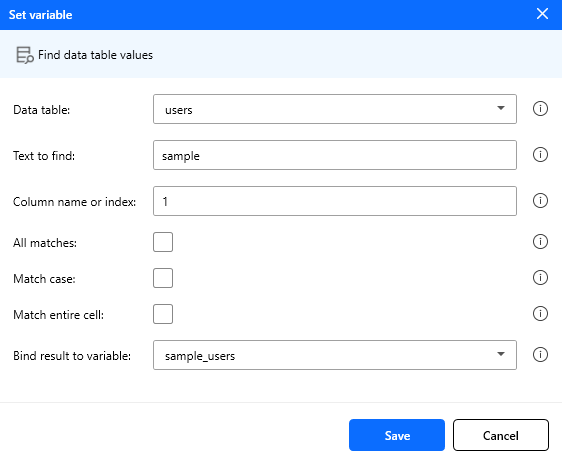
Figure: Find in data table action configuration.
Variables
Variables are placeholders that store values during workflow execution. These values can be reused across different actions, making workflows dynamic and flexible. To reference a variable in another action, use the format %variable_name%, which substitutes the stored value at runtime.
You can see the list of the currently generated variables by clicking on the variables icon at the top right corner of the menu items.
Define a variable
To define a new variable, select the Set variable action from the actions list.
To increase/decrease the value of a numeric variable, select the Increase variable action from the actions list.
Note: Variable names are case sensitive.
Note: The value of a variable can be updated multiple times in different flows.
Note: When setting the value of a variable, make sure that its type is selected correctly according to its use. For example, in loops, the variable must be of type numeric. Otherwise, you will encounter an error when executing the workflow.
Note: When choosing a variable name, make sure that you have not created it before; otherwise, it will be assigned the last value set for it and may cause interference.
Predefined variables
The variables CardId and UserId are reserved; one is the ID of the card tapped on the reader, and the other is the username of the card’s owner.
Variable scope
To use a variable in an action, it must be defined in the previous flows.
When a variable is defined, it remains available throughout the workflow execution.
Variable types
A variable can be of type string, number, or a JSON string. A variable can be assigned different values during the execution of a workflow.
Using variables in actions
To access a variable in an action, use the format %var_name%. For example, if you have defined a variable named username, and you want to fill it in a text field, select the Populate text field action from the actions list, and set the value of the Text to fill-in to %username%. When the workflow is running, it will be replaced with the actual value of the username.
- To access values from a JSON variable, use dot notation.
Example JSON
{> “user”: {> “id”: 123,> “name”: “user1”> }> }
If the variable name is X:
X.user.id -> 123
X.user.name -> user1
- To access values from a data table, use row/column indexing.
Example data table:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 123 | abc |
Syntax:
X[row][columnNameOrIndex]
Examples:
X[0]['id'] -> 123
X[0][1] -> abc
UI Elements
A UI element (User Interface Element) is a distinct, identifiable component of a software interface that an automation process can recognize, interact with, and manipulate during execution. For example, buttons, text boxes, hyperlinks, or images are UI elements.
You can add these elements to the workflow and perform actions (like clicking) on them.
To add UI elements to the workflow, click on the Add UI element button at the top right of the workflow editor window.
UI Element Picker
When you click on the Add UI element, the UI element picker window will appear. You can add UI elements by hovering the mouse cursor over the element. When the red rectangle appears around the element, hold the keyboard Control key and click on the element to add it to the elements list.
Some UI elements contain multiple parts; for example, a button may contain a text element inside it. So make sure that you select the desired element correctly by checking the element name that appears on the top of the red rectangle.
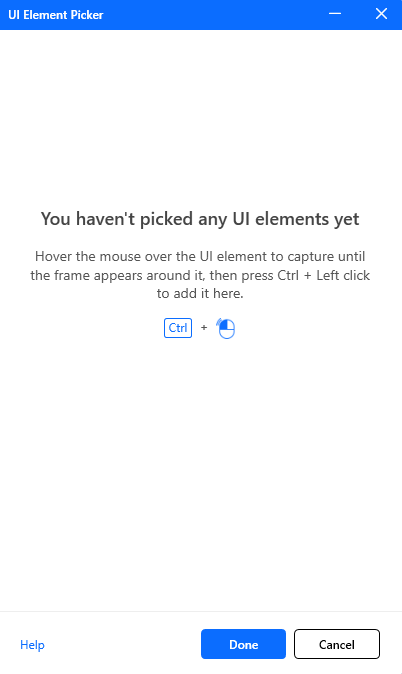
Figure: The UI element picker environment.
Supported UI elements
The supported UI elements are listed below:
- Button
- Input
- Hyperlink
- Check Box
- Combo Box
- Radio Button
- Split Button
- Text
- Image
- Menu
- Menu Item
- Tree
- Tree Item
- Tab
- Tab Item
- List
- List Item
- Data Item
- Header Item
UI Element Selector
UI elements are organized in a hierarchical tree structure, where each element is represented as a node with parent–child relationships. The root node typically corresponds to the application window, and all interface components—such as panels, buttons, and text fields—are arranged beneath it in nested layers. To access or interact with a specific element, the automation process must traverse the correct path through the tree, starting from the root and moving step by step down to the target node.
Therefore, in order to find an element properly, it is necessary to set attributes that will help in the process of finding it. For example, to find a browser window, we can find it by searching for the process name and title of that window.
To edit selectors of a UI element, double-click on the element that exists in the elements tree. The element selector window will appear, which contains:
- Elements: Contains all intermediate elements—such as window, panels, groups, or parent controls—that lead to the target element.
- Attributes: Contains all attributes of the selected element that help in finding the correct element. You can edit the desired attribute’s value.
Note: To exclude an element from the search operation, uncheck it.
Note: To exclude an attribute from matching during search, uncheck it.
Note: If you want to create a workflow that is going to run on other systems, be careful when choosing the selector and attributes so that the values are not dependent on your system. For example, when the root view of an element is a window, the title of that window is tab-dependent, so you can uncheck the Name attribute to avoid mismatches.
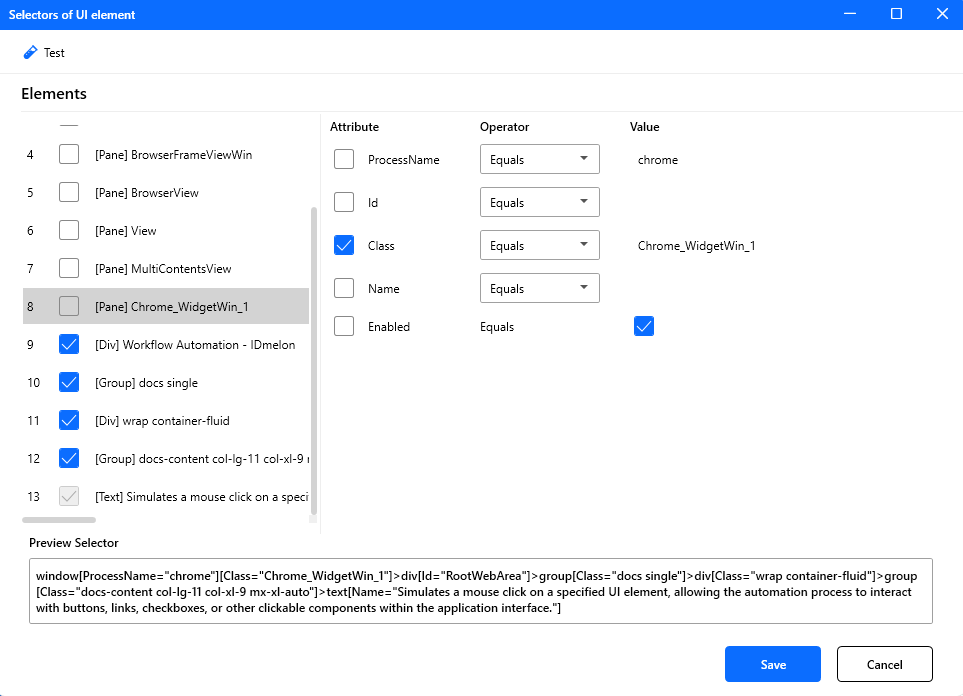
Figure: The UI element selector environment.
Test selectors
To make sure the selector is set correctly, click the Test button at the top of the selector window. If the element is located on the screen, a red rectangle will appear around it.
Deleting a UI element
To delete a UI element from the tree, select the element and press the keyboard Delete key or select the delete option from the context menu. To delete all UI elements of a window, select and delete the window.
Note: When you delete an element, all related flows (element-based actions) will be deleted too.
Flows
A flow is an action with specific parameters and conditions that will be executed one by one when the workflow starts.
You can see the list of flows in the middle section of the workflow editor.
Some commands are defined for flows that you can use by clicking the right mouse button on a selected row or rows.
Below is the list of the available commands:
Run from here
To test the workflow from a specific row, select the target row and then select Run from here.
Moving flows
You can move a flow up or down using the Move up and Move down commands.
You can also move one or multiple flows to any rows using mouse drag and drop. For some special actions like Else if, Else, Next loop, Exit loop, and End block, the order of the flows must be respected.
Copy-Paste flows
You can create duplicates from a flow using copy and paste commands (or Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V shortcuts).
Note: For actions that contain variables, make sure variables with the same name do not cause conflicts.
Disable/Enable flows
If you want to disable a flow temporarily to prevent it from running, select Enable/Disable action.
Note: A disabled flow will be ignored from the exported workflow.
Run/Stop workflow
To test the workflow, click on the Run button, and to stop it, click it again.
Test Selected Action
To test the selected flow, click on the Test selected action button.
Note: When you select multiple flows, this event only affects the first selected flow.
Workflow Runner
Workflow Runner is a tool for running the workflow when the Accesskey Automate Access command triggers.
The app exists in the installation directory in: C:\Program Files\IDmelon\Workflow Automation\WorkflowRunner.exe
Configuring Accesskey
To run a workflow on the security key presence (card tap) trigger, do the following steps:
Export the desired workflow from the Workflow Editor.
Enter the following command in PowerShell to activate the automation.
accesskeycli workflow-automation -s -t automation-app --action execute --workflow-path "PATH_TO_WORKFLOW_FILE"To disable the automation, enter the following command in PowerShell:
accesskeycli workflow-automation -t automation-app -r
Test Workflow
When you have configured everything in the previous section, the workflow must be run when you tap your badge on the reader.
Workflow Runner CLI
Workflow Runner CLI is a tool for running a workflow directly from the command line. This method can be used in Accesskey scripts.
Arguments
| Argument | Value |
|---|---|
| --workflow-path (-w) | The workflow path |
| --variables (-v) | Variables as a JSON string |
To run a workflow using the command line, enter the following command in PowerShell:
workflowrunnercli -w "WORKFLOW_JSON_FILE_PATH"
# Example
workflowrunnercli -w "C:\workflows\login.json"
Pass variables to the workflow as a JSON string using -v in the command line.
workflowrunnercli -w "C:\workflows\login.json" -v "{\"username\": \"xyz\"}"
See Variables for details.
Using the Workflow Runner CLI in the Accesskey script
You can run workflows directly using the Workflow Runner CLI in the Accesskey scripts. Do the following steps to run the workflow on the badge tap.
Export the desired workflow from the Workflow Editor.
Make a new text file, fill it with the following lines, and save it as a .ps1 file.
workflowrunnercli -w "WORKFLOW_JSON_FILE_PATH"Enter the following command in PowerShell to activate the automation.
accesskey config access-automation set --trigger-condition onSecurityKeyPresence --script-path "PS1_SCRIPT_PATH"To disable the automation, enter the following command in PowerShell:
accesskey config access-automation remove all