Availability
Availability is an indicator for a consistent level of a service, which is up and running and usable for its users for prolonged time periods. It can be considered the key indicator of overall service health. Highly available architectures typically through deploying redundant components aim to maximize service availability. Simply put, achieving high availability involves distributing compute resources and replicating data and balancing load between them.
Also, scalability is the system’s ability to handle varying amounts of work by adding or removing resources. The flexibility to adjust the capacity to meet demands and resources consumed by the service as a key business driver moved IDmelon to the Google cloud. Google Cloud helps us maintain a good user experience during periods of high traffic by adding more resources.
To increase availability and scalability of our services, we located them on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and employed Google Cloud tools and services. As a result, IDmelon services work under GCP tools, services, and built-in features. Google Cloud provides multiple features to help build scalable and efficient services which we use as follows:
- Compute Engine virtual machines integrate with auto-scalers that grow or shrink resource consumption based on defined metrics; to distribute and manage instances across the regions and zones.
- Cloud Monitoring provides metrics across services and infrastructure, helping us to make data-driven scaling decisions across our services and infrastructure about their performance.
- Google Cloud Regions and Zones across multiple continents to best meet our availability goals.
- Internal and External Load-Balancing options to manage the service traffic.
Physical distribution of resources
Google Cloud services are available in locations divided into regions and zones across the globe. How an organization deploys its service across these regions and zones affects the availability and latency of the service. Redundancy is the duplication of components of a service or system to increase the overall availability. In Google Cloud, redundancy is achieved by deploying the service in multiple zones or even regions which helps the service to better withstand any disruptions.
IDmelon using Compute Engine, distributes its service in four zones in four different regions. This way we can manage the instances as a logical unit.
Load-balance at each tier
Load balancing distributes traffic among groups of resources. Distributing traffic helps to ensure that individual resources don’t become overloaded while others sit idle. Google Cloud offers several load-balancing choices depending on the type, source, and other aspects of the traffic. It’s a common practice to load-balance requests received from different external sources, such as web or mobile clients. However, using load balancers between different services or tiers within the service can also increase resilience.
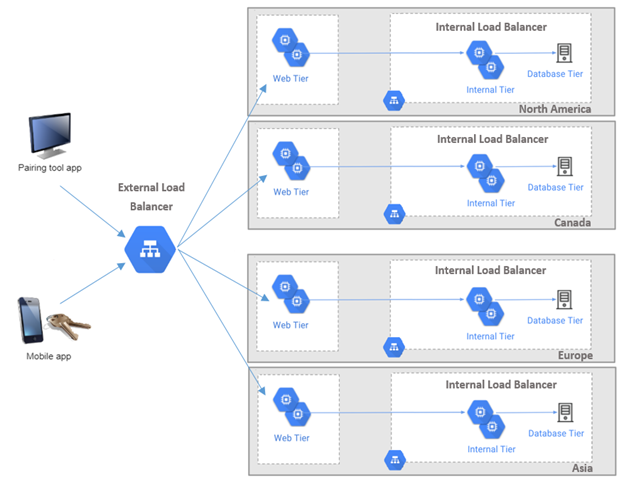
We use an external load balancer to separate traffic of different components (mobile and Pairing Tool). The whole structure consists of four zones in four regions (North America, Europe, Asia, and Canada) with internal load balancing to distribute traffic from the web tier to the internal tier within each region. It also has an external load balancer to divide mobile and Pairing Tool traffic.